- Generative AI, especially ChatGPT, is reshaping the internet, impacting platforms and content quality.
- Issues like model collapse and misinformation highlight the need for careful AI management.
- The current situation underscores the importance of human intervention in AI development and data management.
November 24, 2023: James Vincent of The Verge paints a vivid picture of the current internet landscape, drastically altered by the advent of generative artificial intelligence.
With platforms undergoing major transformations, we’re witnessing the decline of traditional web structures and the rise of AI-driven content.
From Google attempting to overhaul its search results to Twitter’s bot and verification issues, the changes are widespread. Amazon and TikTok face content quality challenges, while online media companies grapple with layoffs. The employment sector is also affected, with the demand for “AI editors” capable of producing hundreds of articles weekly.
ChatGPT, a prominent player in this shift, has been utilized to create entire spam websites. Platforms like Etsy are inundated with AI-generated products, and misinformation is rampant as chatbots cite each other. LinkedIn’s use of AI to engage users, Snapchat and Instagram’s bot-based interaction strategies, Reddit’s blackouts, Stack Overflow’s moderator strikes, the Internet Archive’s battle against data scrapers, and Wikipedia’s internal struggles all signal a seismic shift in the web’s fabric.
The widespread use of text generated by large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT wasn’t unexpected. Initially, the problems seemed minor: increased workloads for moderators, ad clutter in social feeds, and legal issues due to unreliable AI-generated case law.
But these are symptoms of a deeper issue. Every piece of AI-generated text demands a rigorous fact-check, consideration of plagiarism, and policy deliberations.
Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, acknowledged the limitations of GPT-4, noting its initial impressiveness diminishes with prolonged use. Despite its capabilities, the consensus is that it’s contributing to the web’s deterioration.
Two recent studies have raised significant concerns:
- Amazon’s Mechanical Turk: Researchers found that nearly half of the platform’s workers used LLMs for text-based tasks, like summarizing medical research papers. This reliance on AI-generated content threatens the authenticity of crowdsourced human insights.
- Training AI on Synthetic Data: A collaborative study by universities including Oxford, Cambridge, Toronto, and Imperial College London revealed that AI systems trained on synthetic data degrade over time. This “model collapse” poses a real threat to the internet’s integrity.
We’re witnessing an AI ouroboros, where models trained on their own outputs progressively degrade. Research indicates that GPT-4’s capabilities, for example, have diminished over time.
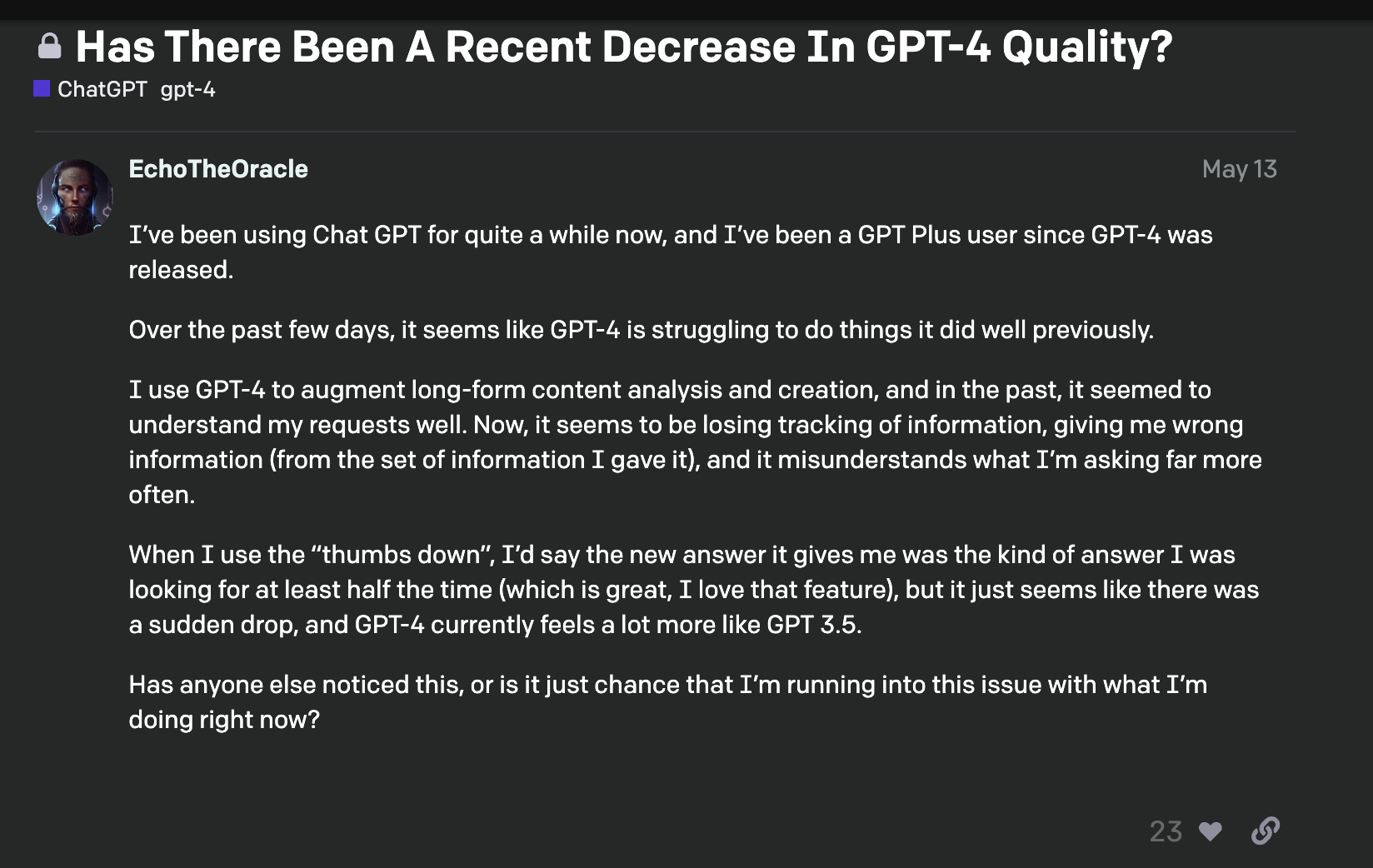
This autophagy, caused by a lack of fresh data, highlights the importance of preserving original datasets for optimal model performance.
The influx of AI-generated content poses challenges:
- Internet Reliability: As AI content fills the web, distinguishing between human and machine-generated text becomes crucial.
- Model Collapse: The reliance on synthetic data for training could lead to model breakdown.
- Research Focus: Identifying and filtering synthetic data from training sets is now a major research area.
Well, generative AI models like ChatGPT have revolutionized content creation but also introduced complexities.
The internet is evolving into a space where AI-generated content is ubiquitous, raising questions about authenticity and sustainability.
As we navigate this new terrain, the need for human oversight and intervention in AI development and deployment becomes increasingly evident.
So what do you all think? Comment down below.